What is Autism?
Autism is a developmental disability which causes significant social, communication, medical, and behavioral challenges. Because autism is a spectrum disorder, the combination of symptoms and their level of severity varies from person to person.

What are the signs & symptoms?
Diagnosis criteria for autism is specific, a person must exhibit the following symptoms to a degree that significantly impairs their daily living:

Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction

Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities
1:0
children have autism in the US
children have autism
in the US
since 2000,
autism
prevalence has
increased
0%
since 2000,
autism
prevalence has
increased
0%
prevalence
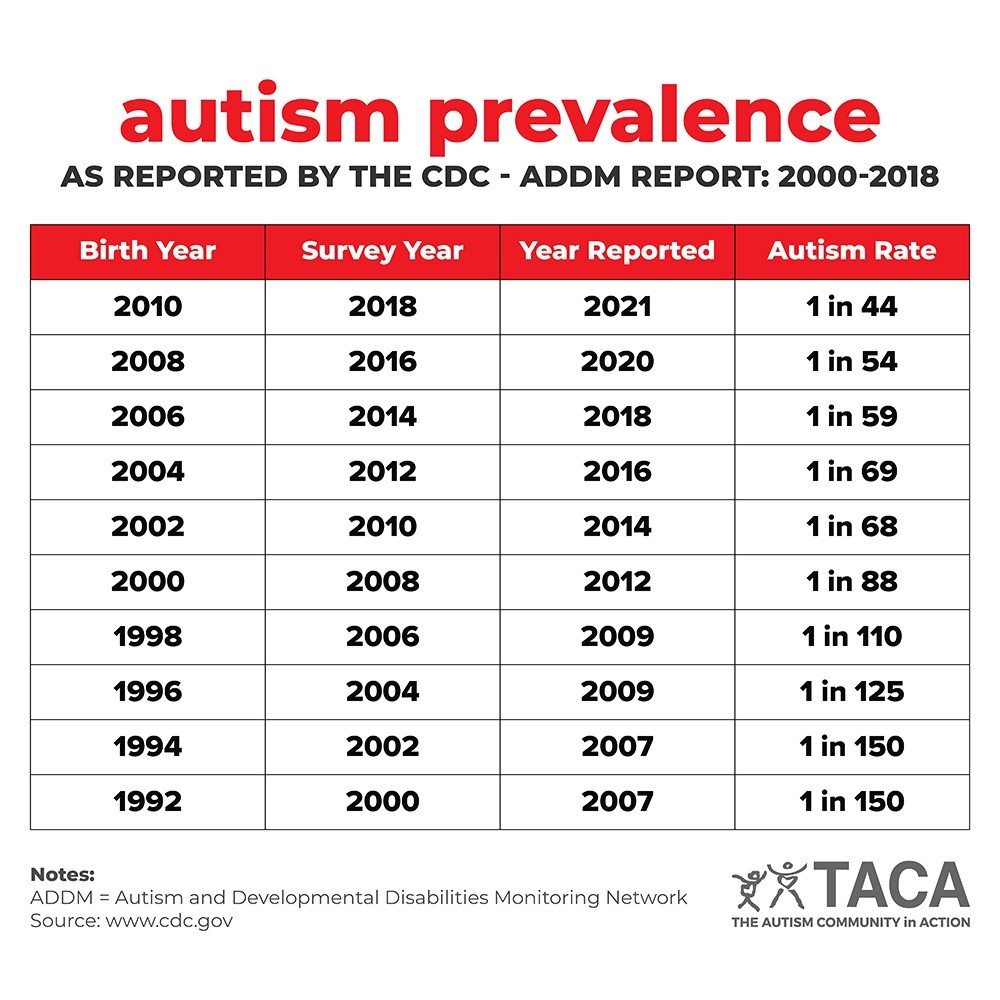
The CDC tracks autism prevalence in the U.S. to better understand the scope and impact autism has upon children, families, and communities. Additionally, service providers and organizations use these findings when preparing to meet the support needs of the families they serve.
This is key information from the CDC's most recent autism prevalence report, as well as answers to some frequently asked questions about autism prevalence.
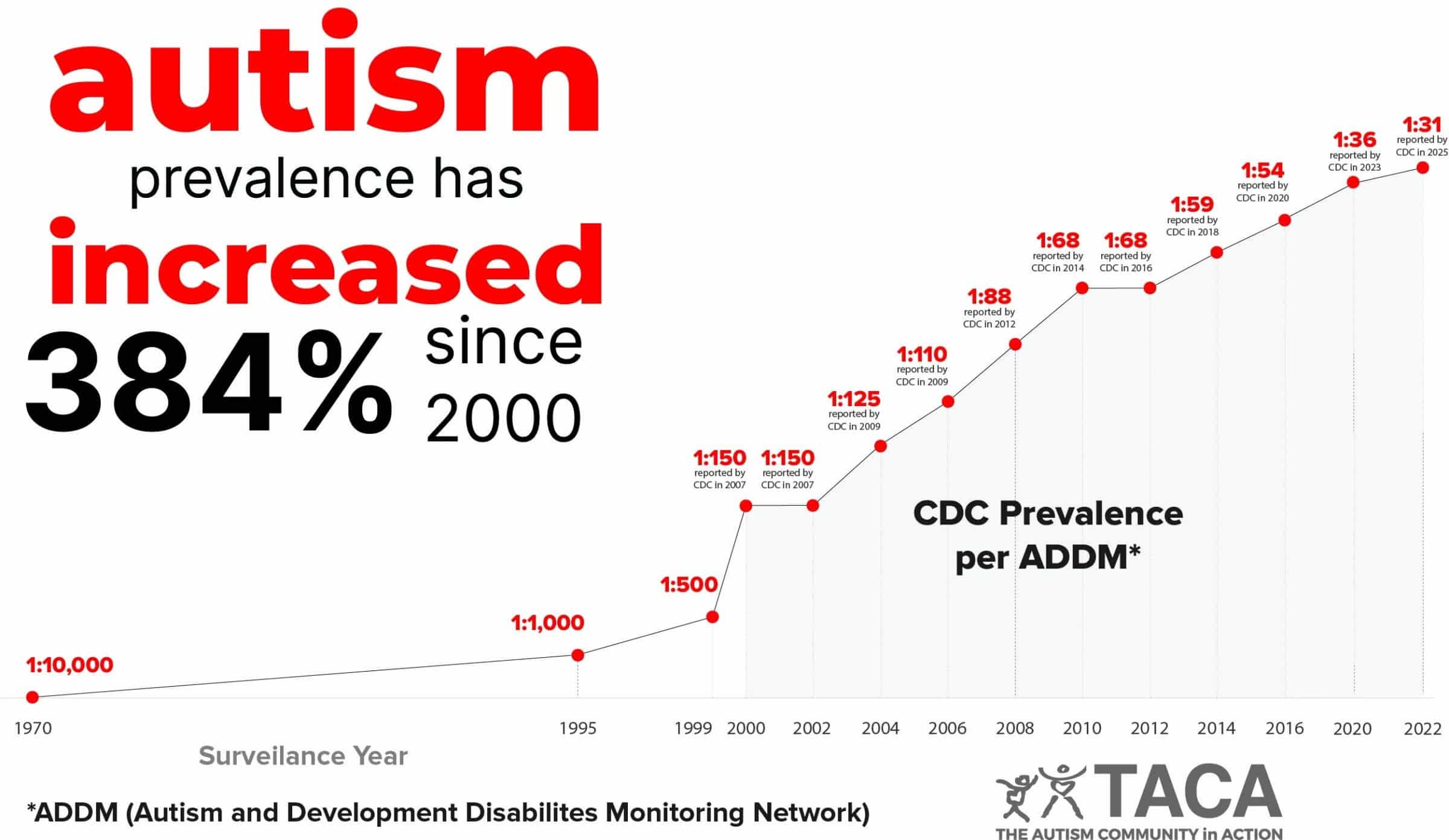
Current Autism Prevalence in the US
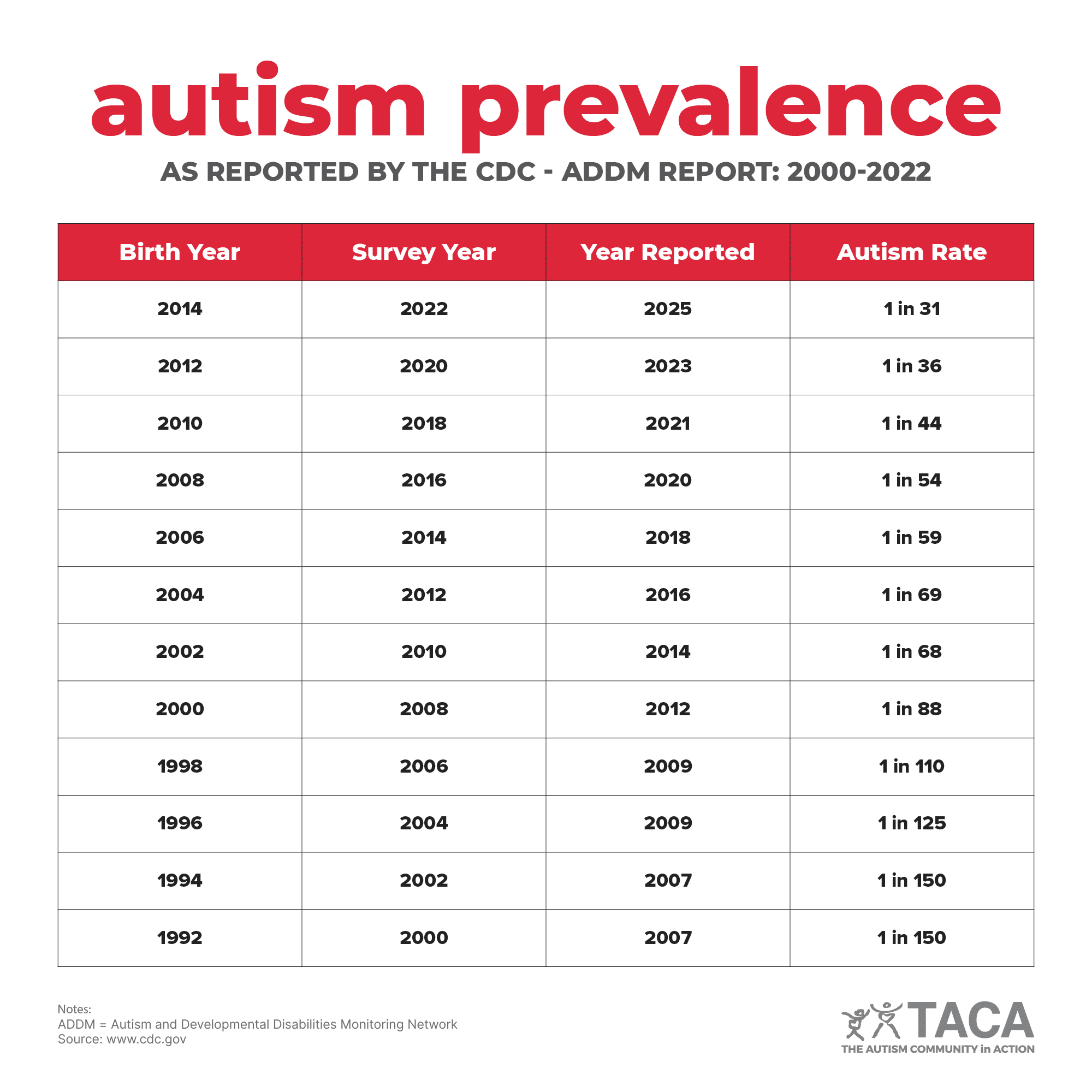
The newly released report by the CDC estimates that 1 in 31 children have autism in the United States, indicating a 384% increase in autism prevalence since 2000 when autism prevalence was 1 in 150.
FAQs
While the cause of autism remains unclear, current studies show genetics and environment both play a role. The CDC also acknowledges that there are "many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors," which is why they have launched the SEED study to learn more about the risk factors and causes of autism.
No. While it is true that the definition of autism was expanded to include PDD-NOS and Asperger's, the CDC states that:
"It is unclear exactly how much of this increase is due to a broader definition of ASD and better efforts in diagnosis. However, a true increase in the number of people with an ASD cannot be ruled out. We believe the increase in the diagnosis of ASD is likely due to a combination of these factors.
We do know that ASD are more common than we thought before and should be considered an important public health concern. There is still a lot to learn about ASD. In addition, increased concern in the communities, continued demand for services, and reports estimating a prevalence of about 1.7 percent show the need for a coordinated and serious national response to improve the lives of people with ASD.”
National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019) Frequently Asked Questions: Is there an ASD Epidemic? Retrieved from www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/topics.html.
The prevalence rate that is considered “official” is the one that is released by the CDC. Other organizations, such as the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH) and the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), use different methods to collect their data and look at different age groups when determining prevalence rates. This is why their autism prevalence rates differ from the CDC’s.
Prevalence rates are not a census. They do not represent the entire population of children with autism in the United States. They are an estimate based on a sampling of communities throughout the United States.
The CDC calculates autism prevalence based on the following data:
- Health and special education records of 8-year-old children
- These records were collected from specific sites located in Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, Missouri, New Jersey, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Wisconsin.
![]()
The CDC collected the data to determine the current rate back in 2022. It takes the CDC about 4 years to analyze the data and release a new prevalence rate.
reports
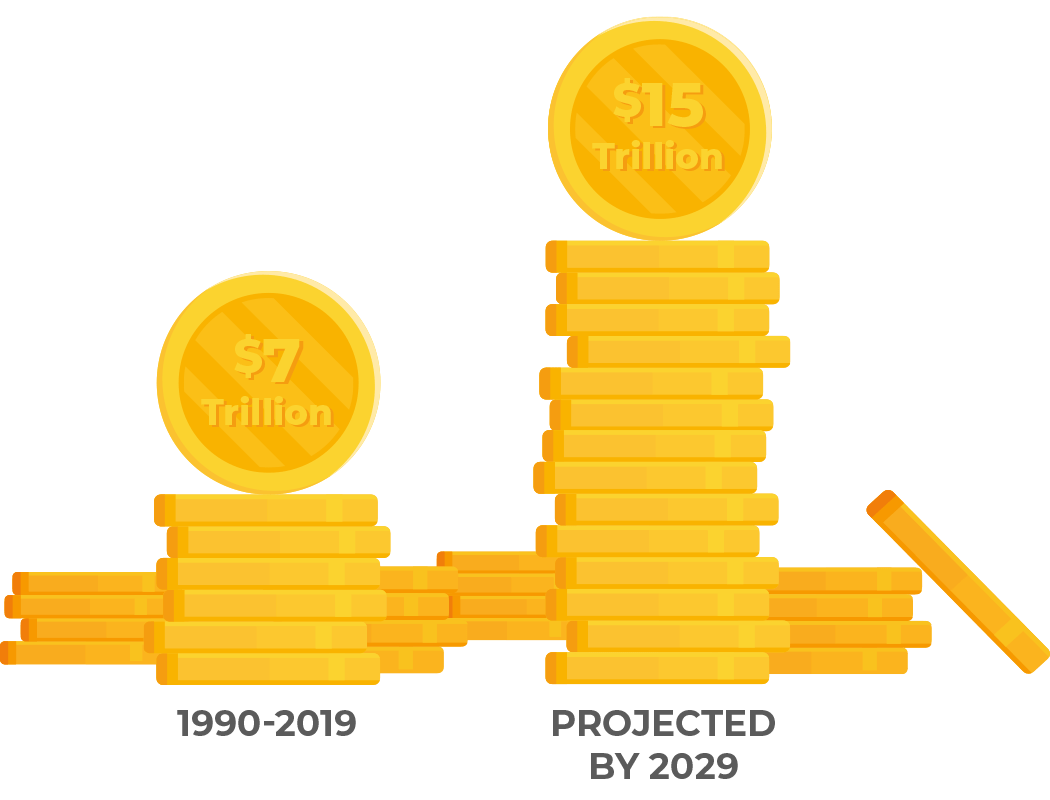

lifetime social cost
Social costs associated with autism for 1990-2019 are estimated at $7 trillion dollars. If the rate of increase in prevalence continues, costs to society could reach nearly $15 trillion by 2029. These estimates only reflect what society pays, not the additional expenses families incur out of their own pockets.
*Research studies are based on children
and adolescents with autism

0%
0%
of children have co-occuring conditions
on average has 4.9*


age 0
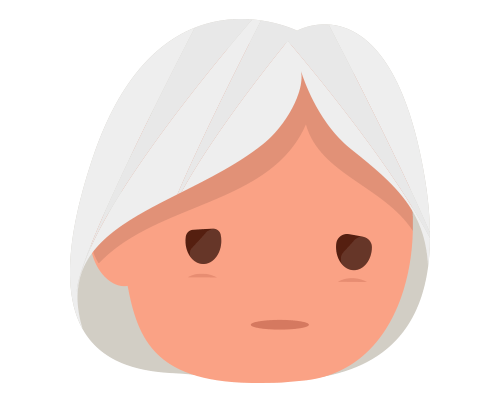
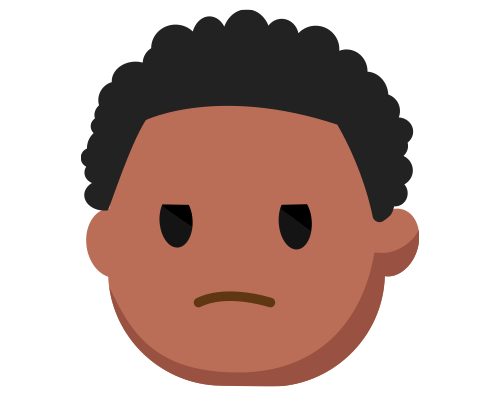
is the average life expectancy of an individual without autism

age 0
is the average life expectancy of an individual with autism
0%
0%
of adults with autism have paid jobs in community-based settings

These are all sobering statistics, but there’s hope because...
we can create a brighter future
effective therapy & medical intervention improves the outcome and quality of life
our programs are designed
to meet these goals
Virtual Support & Education Events
TACA offers monthly virtual parent support and family panel meetings where parents can connect with other autism parents…
Mentor Program
For more individualized support, parents can be matched with an experienced and supported TACA Parent Mentor to help…
Hope & Help for Autism Facebook Group
Hope & Help for Autismfacebook group A great place to find resources, support, help, and hope TACA’s private Facebook Group…
Monthly Learning Series
Discover TACA Through Each Month’s Focus At TACA, we believe in providing comprehensive support and education to families touched by…
Resources
TACA provides in-depth, comprehensive information and resources to help parents navigate all aspects of the autism…
Communities & Family Events
TACA chapters across the US hold meetings, autism learning seminars, coffee talks, and family events…
Conferences
Annually, TACA hosts a parent conference featuring expert speakers from across the United States. Presentations focus…
Scholarships
TACA provides national or regional scholarships as funding is available to assist in financing functional medicine doctors…
Southern California Outreach
TACA’s national headquarters office is located in Irvine, California, and has the capacity to provide extended in-person resources…