Supporting a Healthy Pregnancy

All contents of this resource were created for informational purposes only and are not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician, therapist, or other qualified health providers with any questions or concerns you may have.
Research tells us that if you have one child with autism, you have a 8.4 times higher risk of having a second child diagnosed with autism.
At TACA, we adore our children with autism. They are our very worlds. Even still, research shows that our kids with autism have numerous co-existing medical issues which make their lives challenging in many ways. Therefore, parents often wonder if there are things that can be done to mitigate the risk of having a child with autism. While there are never any guarantees, this article will outline the research and considerations.
This article will cover:
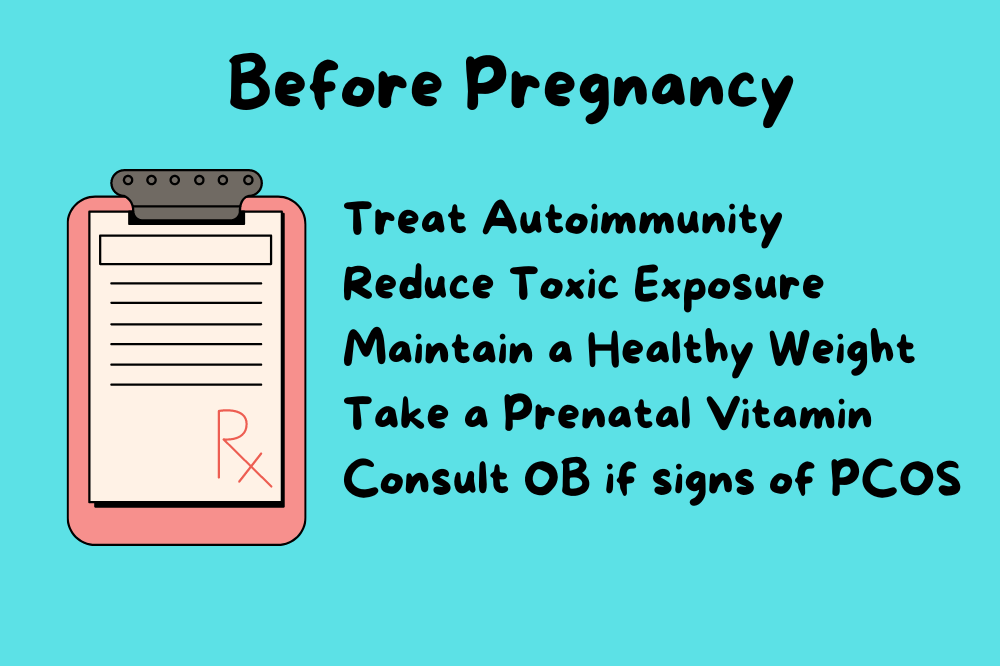
Before Pregnancy
Pregnancy is tough on the body, and addressing your medical issues before becoming pregnant could result in the best possible results for your health, the pregnancy, and your child.
Treat autoimmunity
- Autoimmunity in mothers is linked to autism in children.
- Have autoimmunity well-controlled before conceiving.
- Examples of autoimmunity are Type 1 Diabetes; Thyroid disease such as Hashimotos or Graves; GI disorders such as Crohn’s, Colitis or IBS; Rheumatoid arthritis; MS; Psoriasis; Eczema; and many more.
- Make sure to check ALL thyroid numbers (TSH, Free T3, Free T4, and all antibodies)
Reduce Toxic Exposure
- Don’t smoke
- Move away from air pollution
- Maternal exposure to all pollutants is associated with an increased risk of ASD
- This 2021 study took blood from 214 mothers (mid-pregnancy) who live in California’s Central Valley, showing the worst air quality.
- Researchers identified the metabolic profiles for 116 mothers of babies who later developed ASD and 98 control mothers. Interestingly, results revealed metabolic markers that show mitochondrial dysfunction in the mothers of kids with ASD.
- This is interesting because based on research, the majority of kids diagnosed with autism have mitochondrial dysfunction.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Take a prenatal multivitamin
- Make sure the multivitamin includes bioavailable forms of vitamins such as:
- Folinic acid or 5MTHF (instead of folic acid)
- Methyl B12 instead of cyanocobalamin
- D3 instead of D2
- Examples include:
- Seeking Health Prenatal
- Thorne Prenatal
- New Chapter Prenatal
Consult with your obstetrician if you have signs of PCOS
- Research shows there is an increased risk of autism in babies if the mother has Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- “The autistic traits in the offspring of PCOS patients might be related to the parental high delivery age and high tendency to autism traits.”
During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can be an overwhelming and wonderful experience. See the tips below to optimize your health during pregnancy.

Recommended Interventions
- Check all your medications with your doctor to be sure they are safe.
- Eat a healthy, organic diet
- Reduce Stress
- Drink Filtered water
- Also, do not use water sold in plastic bottles.
- Microplastics found in water are a potential risk factor for autism.
- Maternal exposure to polyethylene micro- and nanoplastics impairs umbilical blood flow.

Things to Avoid
- Avoid Smoking
- Avoid Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Tylenol depletes glutathione which is the body’s biggest antioxidant and also depletes sulfur stores.
- A 2019 study out of John Hopkins University, funded by the NIH showed that the babies with the highest exposure to Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in the womb had 3.62 X higher risk of developing Autism.
- Paracetamol use during pregnancy — a call for precautionary action
- Avoid Folic acid – instead use folinic acid or 5MTHF
- Folic acid is an oxidized, synthetic form of folate that some people have a hard time utilizing.
- Due to several factors, mothers-to-be should take a bioavailable form of folate. Factors include:
- Polymorphisms in certain SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) such as FOLR2, DHFR, SLC19A1, MTHFR, and others.
- An autoimmune condition where there are antibodies that block folate from entering the cells.
- Folinic acid or 5MTHF are more bioavailable forms of folate (B9)
- Try to avoid a C-Section delivery
- When a baby is delivered via C-section, they do not get the benefit of being exposed to their mother’s flora in the vaginal canal.
- Of course, there are circumstances where a C-Section is necessary for the safety of the baby and the mother.
- Compared with babies born by vaginal delivery, babies born via cesarean delivery had increased odds of autism and ADHD.
- Avoid Processed Food
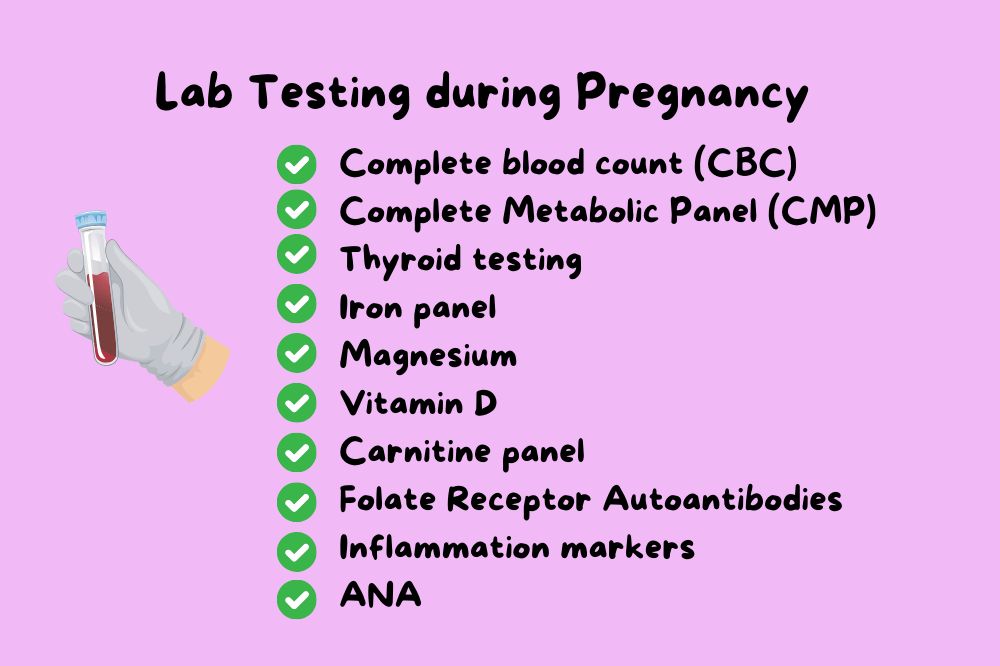
Labs to Run
Recommended supplements
Based on research, there are some very important supplements that should be considered.
Prenatal vitamin with active forms of:
- Active form of B12 (methyl B12)
- folate (5MTHF or folinic acid)
- RESEARCH: When studied, moms of children with autism have several significantly different metabolite levels compared to mothers of typically developing children. Most of the variances were linked to low levels of folate, low vitamin B12, and low Carnitine-conjugated molecules.
- RESEARCH: Children whose mothers reported taking prenatal vitamins during the first month of pregnancy were less likely to receive an Autism diagnosis
- RESEARCH: Statistically significant associations between maternal vitamin supplement use before and/or during pregnancy and reduced risk of autism spectrum disorder in offspring were observed.
- RESEARCH: In 2018, a study was released showing very elevated levels of B12 and folic acid in blood were associated with a higher risk of autism. However, this is not the end of the story. If you are not taking the bioavailable form of B12 and folate, these incorrect forms can float around in the blood, unable to be absorbed. Or worse, these forms may block the absorption of these vitamins. This research did not study people taking methyl B12 or 5MTHF instead of folic acid.
- Read more about Methyl Vitamin B12 for Autism.
- Read more about Cerebral Folate Deficiency in Autism.
Vitamin D3
- Vitamin D during pregnancy is important to reduce inflammation, improve fetal growth, and reduce the risk for preeclampsia, preterm birth, gestational diabetes, and autism.
- RESEARCH: Pregnant mothers deficient in Vitamin D at mid-gestation had more than 2x increased risk of having a child with autism.
- RESEARCH: Pregnant mothers prescribed 5000 IU Vitamin D per day had a lower risk of having a second child with autism.
- RESEARCH: Higher Vitamin D concentrations early in life and higher doses of maternal vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy may have a positive association with neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Iron
- Adequate iron is important during pregnancy to provide enough oxygen to your baby, and reduce risk of autism.
- Dosage is always based on current blood iron and ferritin levels
- RESEARCH: Anemia diagnosed earlier in pregnancy (≤30 weeks) was significantly associated with increased offspring risk of autism spectrum disorder, ADHD, and intellectual disability.
- RESEARCH: Higher iron intake during pregnancy was associated with reduced autism risk.
Omega 3 fish oil (EPA + DHA)
- Omega 3 fatty acids are the critical building blocks of the baby’s brain and retina.
- Make sure your supplement is molecularly distilled.
- RESEARCH: Mothers consuming more total omega-3 in the second half of pregnancy were 40% less likely to have children with autism spectrum disorder
- RESEARCH: Lower prenatal Omega 3 to Omega 6 ratio is associated with more child autistic traits.
- RESEARCH: Pregnant mothers in the lowest 5% of Omega 3 fatty acid intake had a significant increase in offspring autism risk.
- RESEARCH: Parental fish consumption is beneficial for the prevention of Autism and Intellectual Disability.
Active form of folate (folinic acid or 5MTHF)
- Folate helps form the baby’s neural tube which forms the early brain and spine.
- This supplement is most helpful if taken BEFORE pregnancy and in the first trimester.
- There is often not enough in a prenatal
- RESEARCH: Folate autoantibodies have been implicated in blocking folate transport to the fetus in pregnant mothers.
- RESEARCH: Folate autoantibodies (that block folate from getting into the cell) may prohibit a successful pregnancy.
- Read the TACA article about Cerebral Folate Deficiency in Autism.
L-Carnitine or Acetyl-L-Carnitine
- Carnitine plays an important role in energy metabolism which is needed to transport essential nutrients to the fetus.
- RESEARCH: Problems with long-chain fatty acids in the nervous stem cells of the developing brain caused by L-carnitine deficiency increases the risk of developing ASD in the fetus.
- RESEARCH: “Abnormal biomarkers indicating mitochondrial dysfunction is more common in patients with autism than in the general population. L-carnitine is necessary to transfer long-chain fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria through the internal mitochondrial membrane for β-oxidation”
- RESEARCH: Carnitine levels in the blood declines during pregnancy.
Choline
- Choline is needed for healthy brain development.
- RESEARCH: Data shows that the majority of pregnant women are not consuming adequate choline levels. Also, certain common genetic variants may increase requirements for choline beyond current recommendations.
- RESEARCH: “Seven-year-old children performed better on a challenging task requiring sustained attention if their mothers consumed twice the recommended amount of choline during their pregnancy.”
- RESEARCH: “Maternal choline supplementation during pregnancy may enhance fetal brain development and improve early signs and symptoms that may predispose to mental illness.”
Magnesium
- Magnesium is needed to fuel over 300 processes in the body. It may also reduce the risk of preeclampsia and increase birth weight
- There are numerous forms of magnesium. Choose one that helps raise levels of magnesium in the blood.
- More on magnesium forms in this TACA article on Nutritional Deficiencies in Autism.
- Too much magnesium can deplete other electrolytes such as potassium, so be sure to monitor intake.
- RESEARCH: Magnesium levels in pregnant women may affect the length of gestation and help reduce preterm birth.
Calcium
- Calcium-rich foods are important to prevent preeclampsia and preterm birth.
- If you are not eating foods such as leafy greens, broccoli, oranges, and calcium-rich water, then supplementation is necessary.
- RESEARCH: Maternal supplementation of calcium during pregnancy preparation was associated with decreased ASD risk.

After Delivery
After delivery, enjoying and loving your baby should be your top priority. Here are some other items to consider post-delivery:
Breastfeed (if possible)
- Try to breastfeed for at least 6 months if possible.
- Breastfeeding passes the mother’s antibodies to the baby.
- RESEARCH: There is a 58 % decrease in the risk of autism spectrum disorder with occasional breastfeeding and a 76% decrease risk with exclusive breastfeeding.
- RESEARCH: Children with autism were significantly less likely to have been breastfed than those without autism.
Supplement breastfed babies with Vitamin D
- Breastmilk has insufficient vitamin D to meet baby’s needs.
- 1,000 IU of vitamin D3 for the first 3 years of life.
Infant Probiotics for baby
- Infants have different gut flora than toddlers age 2 and up. Therefore, they require infant probiotics.
- Specifically, infant Bifidobacterium can be helpful.
- RESEARCH: Infants at elevated risk for autism had less Bifidobacterium and more Clostridium-related species at age 5 months.
Avoid Acetaminophen (Tylenol) for baby
- RESEARCH: Tylenol given to babies before age 2, was found to be associated with autism among male children.
Conclusion
As you can see, there is abundant research to help guide you during your pregnancy. We hope this compilation of the most recent research leads you to a happy, healthy pregnancy and baby.